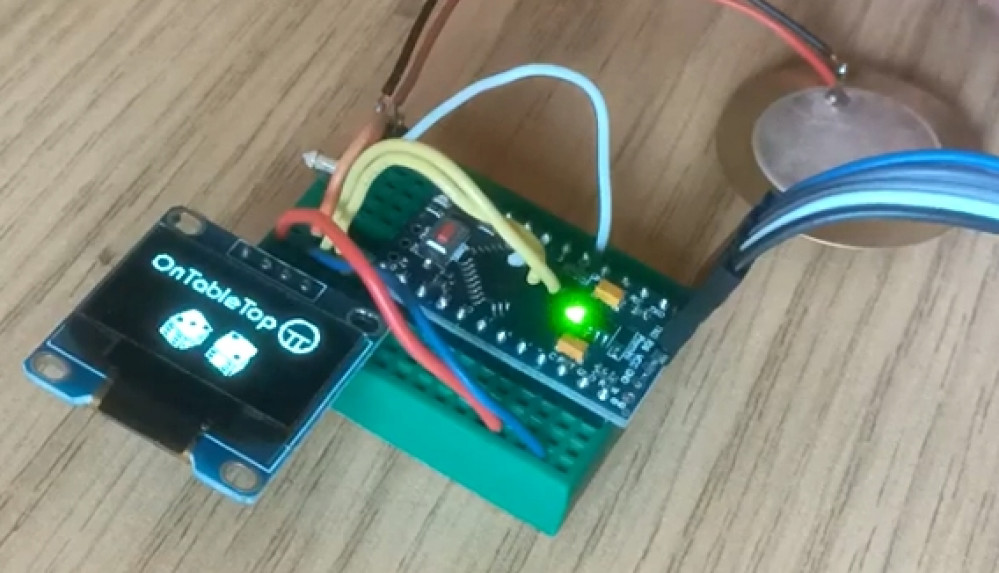
Digital dice roller
Recommendations: 392
About the Project
This is the 21st century, not the Stone Age! Still rolling little shaped bits of bone to generate a bit of randomness in your gaming? Get with the future guys!
Related Genre: Game Aid
Related Contest: Spring Clean Hobby Challenge (Old)
This Project is Active
Give it a whack
What happens when we give a piezo a whack?
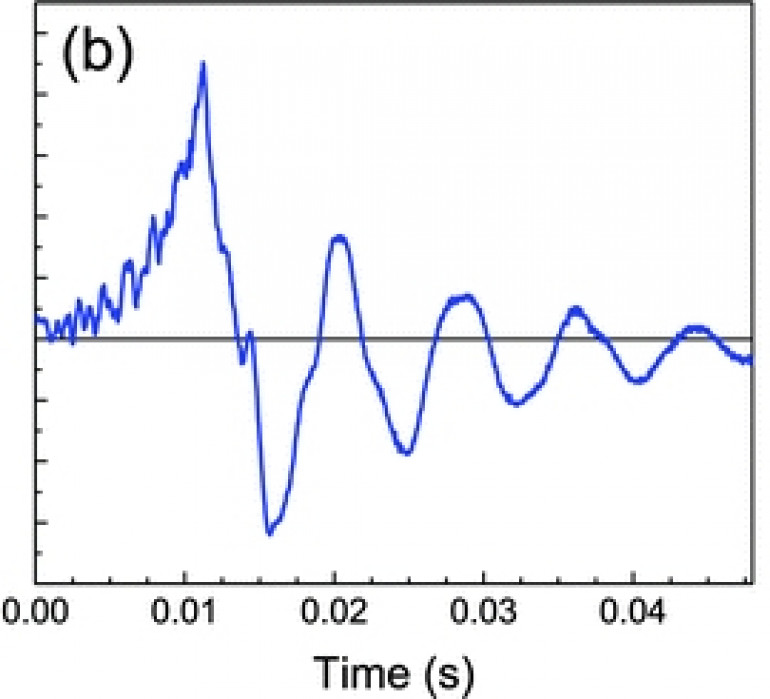
It generates voltage. Maybe only a tiny amount. Maybe quite a large amount. It depends how hard you whack it. Although the current may only be a few milliamps, the voltage can be in the tens of volts
The voltage also goes positive and negative. And repeats, as the signal decays. Give a piezo a hard enough whack and a single hit can produce four, five, six or more detectable “peaks”.
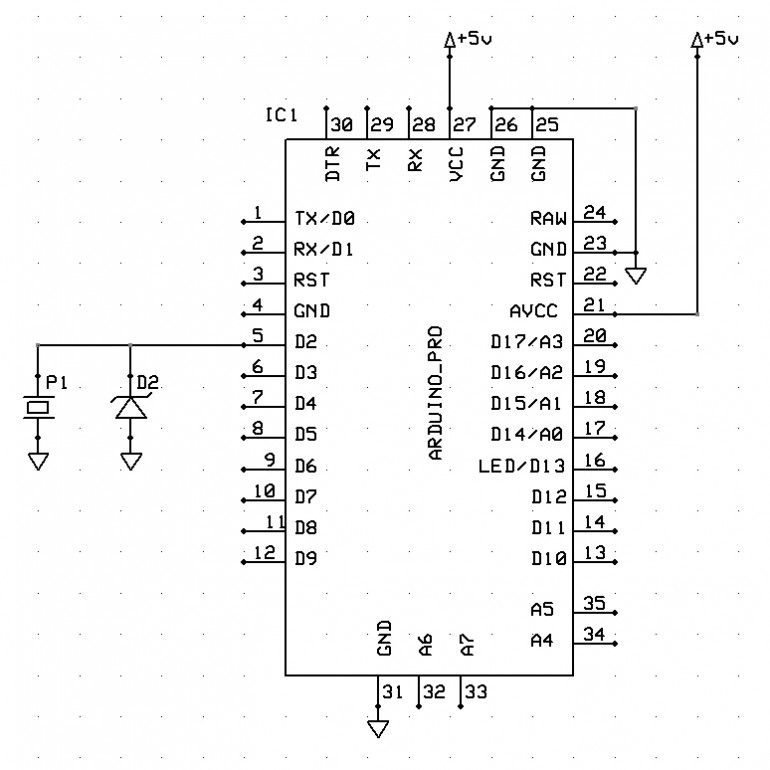
Now microcontrollers (into which we’re planning on feeding such a signal) are sensitive little things (especially the AVR chips that make up the hobby-friendly Arduino development platform) and really don’t like too high a voltage being pushed into them, and they really, really don’t like negative voltages (PIC microcontrollers, with their “clamp diodes” on the i/o pins are far more robust, but we’re sticking with AVR to keep the project “hobbyist friendly”).
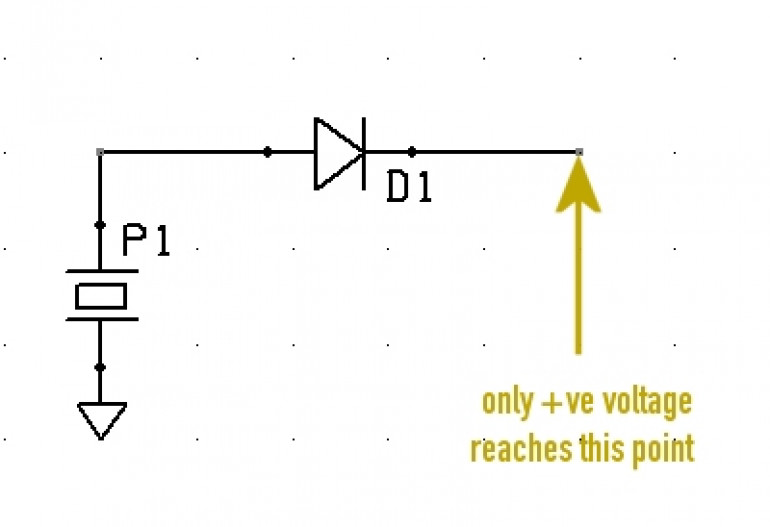
So we need to do two things to this signal – prevent any negative signal from reaching our microcontroller, and peaking the voltage at about 5v.
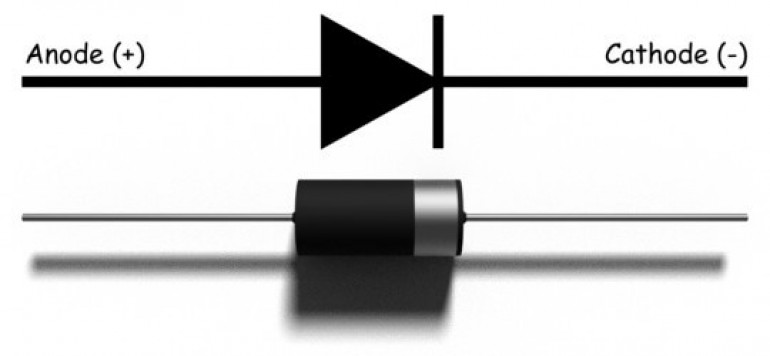
This is a diode. It’s a component that only lets current flow in one direction. It allows current to flow from the anode (positive) to the cathode (negative) terminals, but blocks any negative voltage trying to flow back the other way (hence the little “barrier” mark on the symbol, to indicate that current will be blocked).
Now the above is a very simplified analogy and while not strictly true for the pedants who might want to argue against it, it serves the purpose to demonstrate that positive voltage flows easily through a diode from anode to cathode, but negative voltage cannot.
Interestingly, it is possible for negative voltage to flow “backwards” through a diode (negative voltage on the cathode, marked -ve, can flow through the diode towards the anode, marked +ve).
We can make use of this property, and a special kind of diode to help us achieve our aims: with a zener diode.
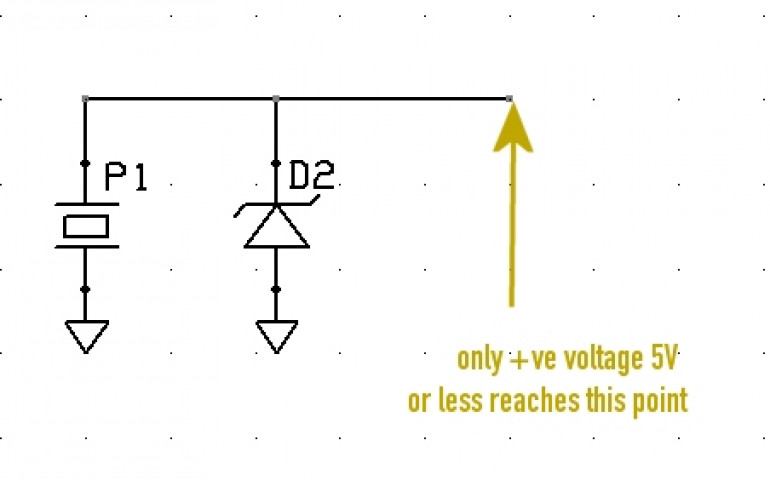
Zener diodes are special in that they act like normal diodes up to a specific voltage. Over this voltage, they “break down” and allow the “excess voltage” to pass through.
Zener diodes have specific values at which they “break down” so by placing a 5V zener diode as in the diagram above, we achieve two things:
If the piezo transducer is creating a negative voltage, this negative voltage is allowed to pass “backwards” through the diode, and will safely go to ground – it does not enter the microcontroller.
Secondly, if the piezo is creating a positive voltage (that we want to capture) any voltage above 5V will also pass through the diode, into ground. This means that the maximum voltage that will reach our microcontroller is positive, up to 5V (it can still be less than 5V).
So this is how we wire the piezo to our Arduino input, ensuring that it is protected from over-voltage and negative voltage, generated by giving the transducer an almighty great whack (hey, who knows which klutz is going to be using these things?)
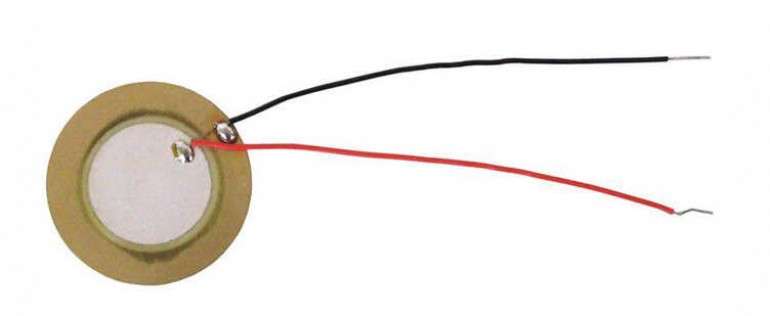
This is a piezo
This is a piezo.
Well, to give it it’s full name, a piezo-electric tranducer. They pop up in lots of things. Mostly in anything that makes a noise.
They’re like a super-cheap alternative to a speaker (but really poor quality). Apply a voltage across the leads and the disc will refract. Do this often enough and you can create a sound. Do it at a specific frequency, and it can play a “note” (though it’s more like an electronic chirp at a specific pitch – calling it a note suggests a degree of musicality that, frankly, it doesn’t posses).
But piezos aren’t just for turning electricity into noise. You can use them to turn noise into electricity. You’ll often find piezo-electric transducers strapped to the body of an acoustic guitar.
The vibrations in the wood of the body are transferred into the disc of the piezo, which is sent to an amplifier, to create an electronic signal (you can get “proper” pickups for electric guitars, which sit underneath the strings, but “piezo pickups” are also common – even through, strictly speaking, they’re not really pickups).
I thought I’d use this property to create a digital dice-roller – some gubbins in miniature base with a battery and a screen, which chose a random number between a range (1-6 for D6, 1-10 for D10) and displayed the result as a bitmap (depicting a dice value) on a tiny LCD screen.
Such a simple object doesn’t need a fancy UI – just a way of telling it “I want a new value now, please”. I figured that tapping the object down on the tabletop would be a perfect way to trigger such a request.
And a piezo would be the perfect way of accomplishing this.

































![How To Paint Moonstone’s Nanny | Goblin King Games [7 Days Early Access]](https://images.beastsofwar.com/2024/12/3CU-Gobin-King-Games-Moonstone-Shades-Nanny-coverimage-225-127.jpg)